Testing Canary Deployment
Automated Canary Promotion
According to the Flagger documentation, canary deployment is triggered by changes in any of the following objects:
- Deployment PodSpec (container image, command, ports, env, resources, etc).
- ConfigMaps and Secrets mounted as volumes or mapped to environment variables
We will trigger a canary deployment by updating the container image of detail service to version 2. Flagger will detect changes to the target deployment and will perform a canary analysis before promoting the new version as primary.
export APP_VERSION_2=2.0
kubectl -n flagger set image deployment/detail detail=public.ecr.aws/u2g6w7p2/eks-microservice-demo/detail:${APP_VERSION_2}
Flagger detects that the deployment revision changed and starts a new rollout. You can see the log events for this deployment
kubectl -n appmesh-system logs deploy/flagger --tail 10 -f | jq .msg
You can also check the events using the below command
kubectl describe canary detail -n flagger
When the canary analysis starts, Flagger will call the pre-rollout webhooks before routing traffic to the canary. Note that if you apply new changes to the deployment during the canary analysis, Flagger will restart the analysis.
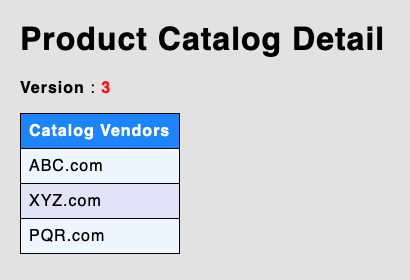
Go to the LoadBalancer endpoint in browser and verify if new version 2 has been deployed.
Automated Rollback
We will create the scenario for automated rollback. During the canary analysis we will generate HTTP 500 errors to test if Flagger pauses the rollout.
Trigger a canary deployment by updating the container image of detail service to version 3:
export APP_VERSION_3=3.0
kubectl -n flagger set image deployment/detail detail=public.ecr.aws/u2g6w7p2/eks-microservice-demo/detail:${APP_VERSION_3}
Once the canary analysis starts, you see the below message
kubectl -n appmesh-system logs deploy/flagger --tail 10 -f | jq .msg
Exec into the loadtester pod
kubectl -n flagger exec -it deploy/flagger-loadtester bash
Generate HTTP 500 errors from http://detail-canary.flagger:3000/catalogDetail
curl http://detail-canary.flagger:3000/injectFault
hey -z 1m -c 5 -q 5 http://detail-canary.flagger:3000/catalogDetail
When the number of failed checks reaches the canary analysis threshold which we have set as 1 in our setup, the traffic is routed back to the primary, the canary is scaled to zero and the rollout is marked as failed.
kubectl -n appmesh-system logs deploy/flagger --tail 10 -f | jq .msg
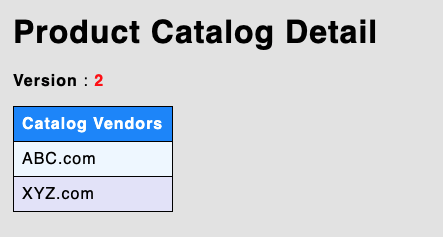
Go to the LoadBalancer endpoint in browser and you will still see version 2 and version 3 did not get deployed.

Redeploy Version 3 again
Lets deploy the version 3 again, this time without injecting errors.
As per the Flagger FAQ you can set an update to an annotation so that flagger knows to retry the release. The canary that failed has already been updated to the new image version 3, which is why setting the image version to the same value a second time will have no effect. So we need to update the annotation of the pod spec, which will then trigger a new canary progressing which is what we will be doing using below yaml.
export APP_VERSION_3=3.0
envsubst < ./flagger/flagger-app_noerror.yaml | kubectl apply -f -
Flagger detects that the deployment revision changed and starts a new rollout:
kubectl -n appmesh-system logs deploy/flagger --tail 10 -f | jq .msg
Go to the LoadBalancer endpoint in browser and verify if new version 3 has been deployed.