Artifact Configuration
Lets configure all the artifacts and storage for Spinnaker services that we will need for our usecase. We will adding all the configuration to the file located at deploy/spinnaker/basic/spinnakerservice.yml which got created by Spinnaker Operator install in previous chapter.
Configure Spinnaker Release Version
Pick a release from https://spinnaker.io/community/releases/versions/ and export that version. Below we are using the latest Spinnaker release when this workshop was written,
export SPINNAKER_VERSION=1.25.4
Open the SpinnakerService manifest located at deploy/spinnaker/basic/spinnakerservice.yml, and change below for Spinnaker Version
Configure S3 Artifact
We will configure Spinnaker to access an bucket as a source of artifacts. Spinnaker stages such as a Deploy Manifest read configuration from S3 files directly. Lets enable S3 as an artifact source.
Spinnaker requires an external storage provider for persisting our Application settings and configured Pipelines. In this workshop we will be using S3 as a storage source means that Spinnaker will store all of its persistent data in a Bucket.
-
Create S3 Bucket first
You can create S3 bucket either using Admin Console or using AWS CLI (Use one of the option from below)
-
Using Admin Console
Go to AWS Console »> S3 and create the bucket as below
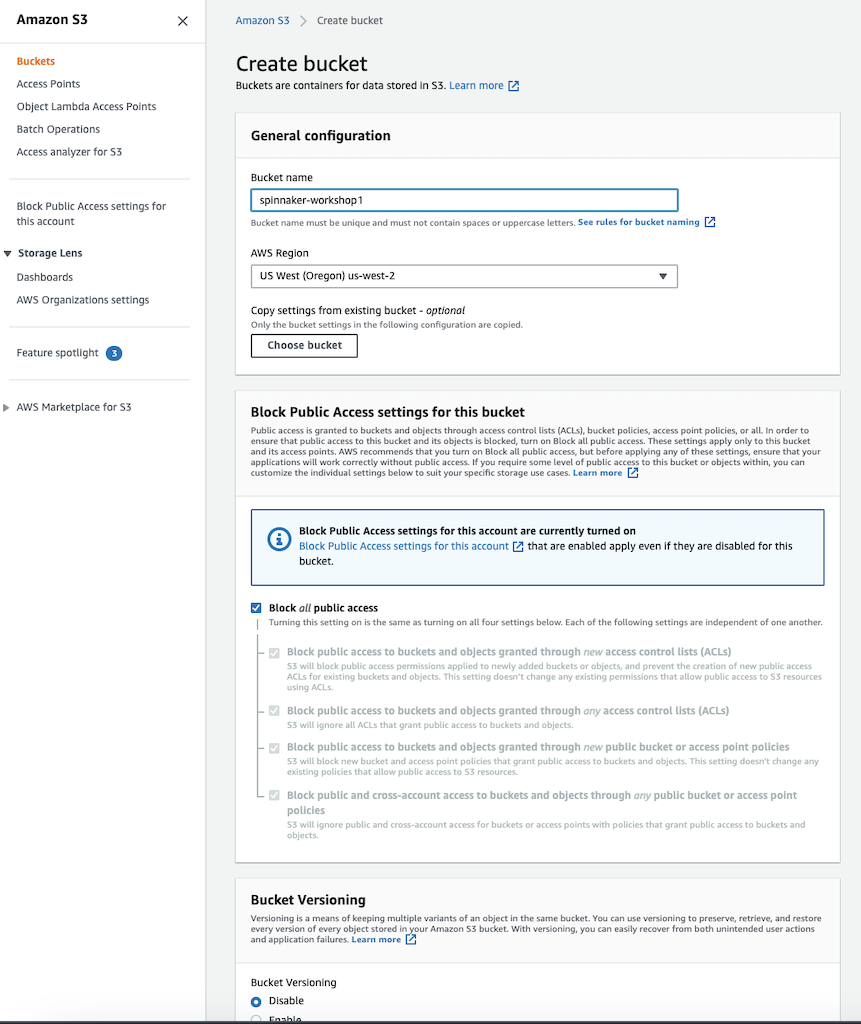
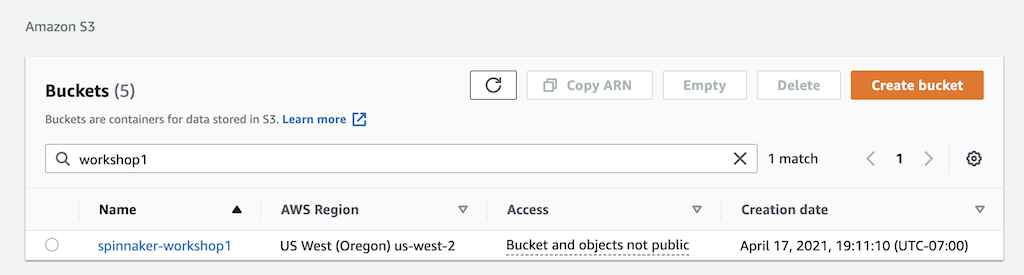
-
Using AWS CLI
export S3_BUCKET=spinnaker-workshop-$(cat /dev/urandom | LC_ALL=C tr -dc "[:alpha:]" | tr '[:upper:]' '[:lower:]' | head -c 10) aws s3 mb s3://$S3_BUCKET aws s3api put-public-access-block \ --bucket $S3_BUCKET \ --public-access-block-configuration "BlockPublicAcls=true,IgnorePublicAcls=true,BlockPublicPolicy=true,RestrictPublicBuckets=true" echo $S3_BUCKET
-
-
Set up environment variables
AWS_ACCESS_KEY_ID and AWS_SECRET_ACCESS_KEY are the AWS profile credentials for the user who has created the above S3 bucket.
- Configure persistentStorage
Open the SpinnakerService manifest located at deploy/spinnaker/basic/spinnakerservice.yml, then update the section spec.spinnakerConfig.config as below.
Configure ECR Artifact
Amazon ECR requires access tokens to access the images and those access tokens expire after a time. In order to automate updating the token, use a sidecar container with a script that does it for you. Since both Clouddriver and the sidecar container need access to the ECR access token, we will use a shared volume to store the access token.
The sidecar needs to be able to request an access token from ECR. The Spinnaker installation must have the AmazonEC2ContainerRegistryReadOnly policy attached to the role assigned in order to request and update the required access token.
- Create ECR Repository
Clone Application Git Repo
cd ~/environment
git clone https://github.com/aws-containers/eks-microservice-demo.git
cd eks-microservice-demo
We need to push a test container image to the newly created ECR repository. The resaon being, empty ECR respository does not show up in the Spinnaker UI when we set up the trigger in pipeline.
export ECR_REPOSITORY=eks-microservice-demo/test
aws ecr get-login-password --region $AWS_REGION | docker login --username AWS --password-stdin $ACCOUNT_ID.dkr.ecr.$AWS_REGION.amazonaws.com
aws ecr describe-repositories --repository-name $ECR_REPOSITORY >/dev/null 2>&1 || \
aws ecr create-repository --repository-name $ECR_REPOSITORY >/dev/null
TARGET=$ACCOUNT_ID.dkr.ecr.$AWS_REGION.amazonaws.com/$ECR_REPOSITORY:latest
docker build -t $TARGET apps/detail
docker push $TARGET
- Create a configmap
Below we are creating the spinnaker namespace where all the Spinnaker services will be deployed and also creating configmap for ECR token.
kubectl create ns spinnaker
cat << EOF > config.yaml
interval: 30m # defines refresh interval
registries: # list of registries to refresh
- registryId: "$ACCOUNT_ID"
region: "$AWS_REGION"
passwordFile: "/etc/passwords/my-ecr-registry.pass"
EOF
kubectl -n spinnaker create configmap token-refresh-config --from-file config.yaml
Confirm if configmap is created correctly
kubectl describe configmap token-refresh-config -n spinnaker
- Add a sidecar for token refresh
Open the SpinnakerService manifest located under deploy/spinnaker/basic/spinnakerservice.yml, then add the below snippet under spec.spinnakerConfig.config.
- Define an ECR Registry
Open the SpinnakerService manifest located under deploy/spinnaker/basic/spinnakerservice.yml, then add the below section under spec.spinnakerConfig.
Configure Igor
Igor is a is a wrapper API that provides a single point of integration with Continuous Integration (CI) and Source Control Management (SCM) services for Spinnaker. It is responsible for kicking-off jobs and reporting the state of running or completing jobs.
Clouddriver can be configured to poll the ECR registries. When that is the case, igor can then create a poller that will list the registries indexed by clouddriver, check each one for new images and submit events to echo (hence allowing Docker triggers)
Open the SpinnakerService manifest located under deploy/spinnaker/basic/spinnakerservice.yml, then add the below section to spec.spinnakerConfig.profiles.
Add GitHub Repository
- Set up environment variables
- Configure GitHub
To access a GitHub repo as a source of artifacts. If you actually want to use a file from the GitHub commit in your pipeline, you’ll need to configure GitHub as an artifact source in Spinnaker.
Open the SpinnakerService manifest located under deploy/spinnaker/basic/spinnakerservice.yml, then add the below under section spec.spinnakerConfig.config.