Run sample workload
Now let’s run a sample workload using one of the inbuilt example scripts that calculates the value of pi.
First get the virtual EMR clusters id and arn of the role that EMR uses for job execution.
export VIRTUAL_CLUSTER_ID=$(aws emr-containers list-virtual-clusters --query "virtualClusters[?state=='RUNNING'].id" --output text)
export EMR_ROLE_ARN=$(aws iam get-role --role-name EMRContainers-JobExecutionRole --query Role.Arn --output text)
Lets start a sample spark job.
aws emr-containers start-job-run \
--virtual-cluster-id=$VIRTUAL_CLUSTER_ID \
--name=pi-2 \
--execution-role-arn=$EMR_ROLE_ARN \
--release-label=emr-6.2.0-latest \
--job-driver='{
"sparkSubmitJobDriver": {
"entryPoint": "local:///usr/lib/spark/examples/src/main/python/pi.py",
"sparkSubmitParameters": "--conf spark.executor.instances=1 --conf spark.executor.memory=2G --conf spark.executor.cores=1 --conf spark.driver.cores=1"
}
}'
You will be able to see the completed job in EMR console. It should look like below:
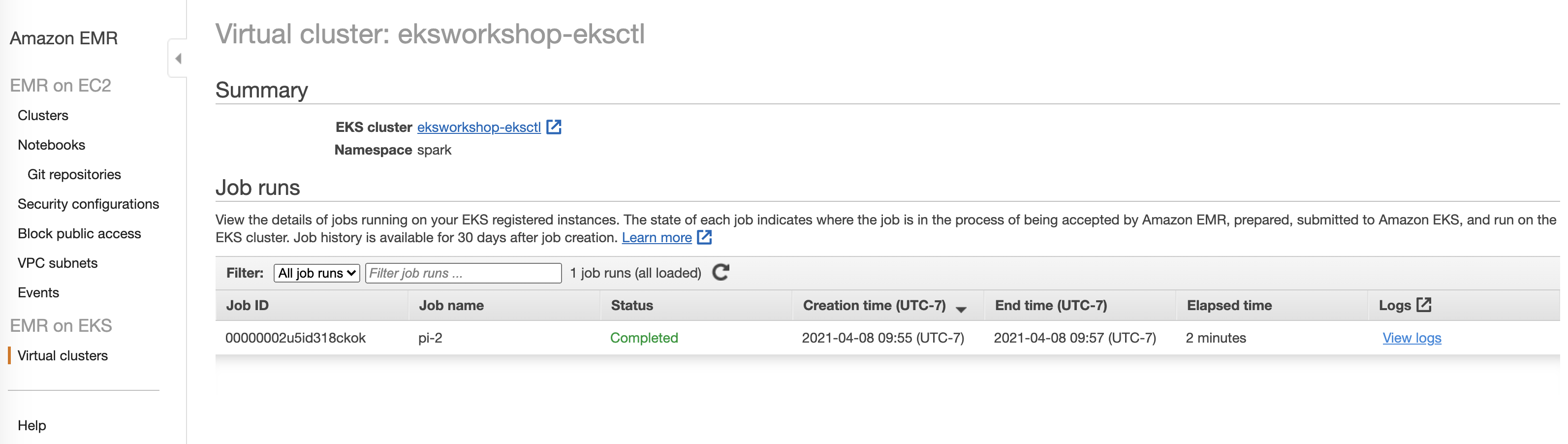
In the next few sections we will cover how to use spark history server to view job history. We will also take a look at how to send logs to s3 and cloudwatch.