About DJ App
Architecture
The example app we’ll walk you through creating on App Mesh is called DJ and is used for a cloud-based music service.
This application is composed of three microservices:
- dj
- metal-v1
- jazz-v1
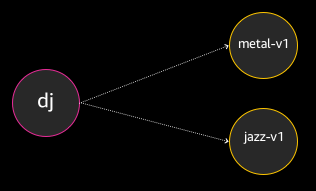
The dj service makes requests to either the jazz-v1 or metal-v1 backends for artist lists:
- Requests made to the
jazz-v1backend may return artists such as Miles Davis or Astrud Gilberto. - Requests made to the
metal-v1backend may return artists such as Judas Priest or Megadeth.
Challenge
Today, dj is hardwired to make requests to metal-v1 and jazz-v1.
Each time there is a new metal or jazz release, we also need to release a new version of dj as to point to its new version-specific endpoints. It works, but it’s not an optimal configuration to maintain for the long term.
Solution
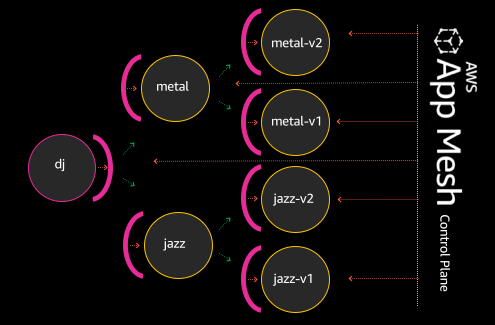
We’re going to demonstrate how AWS App Mesh can be used to simplify this architecture; by virtualizing the metal and jazz services, we can add dynamic configuration and route traffic to the versioned endpoints of our choosing, minimizing the need for complete re-deployment of the dj service each time there is a new metal or jazz service release.
When we’re done, our app will look more like the following: